Daily Current Affairs - May 29th, 2025
Panchayat Advancement Index
- It is India’s first framework to evaluate the performance of Gram Panchayats (GPs) on key development indicators.
- Launched by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, this tool aligns with the
- localization of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to promote evidence-based rural governance and policy intervenƟ interventions for over 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats Panchayats across the nation.
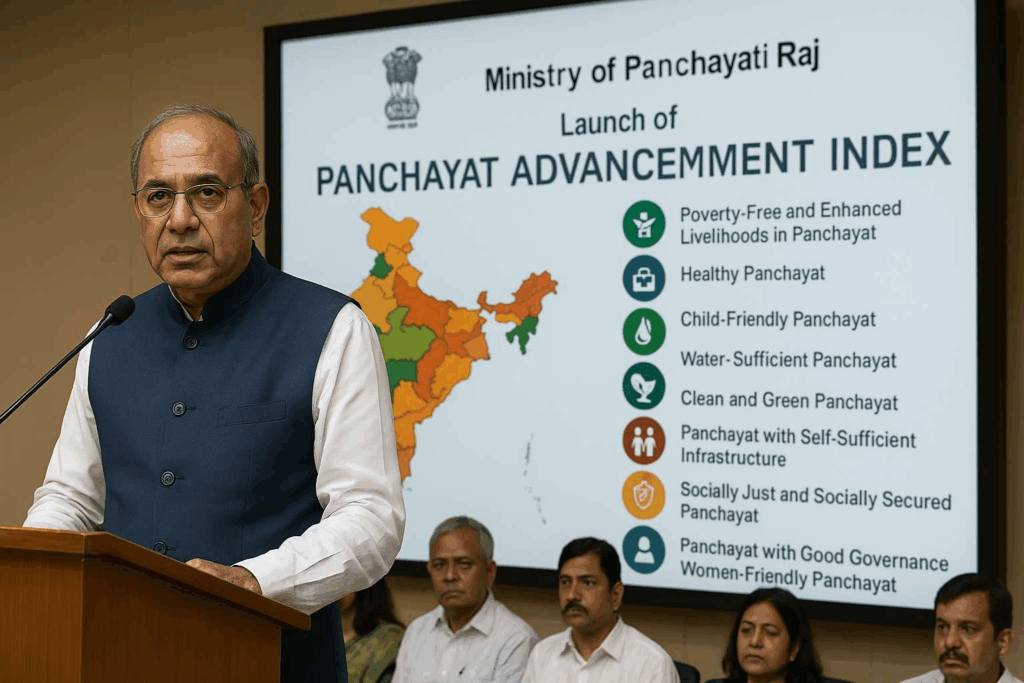
- PAI is a composite performance assessment index designed to measure the effecƟ effectiveness of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in service delivery, governance, and sustainable rural development.
- Launch: The first PAI Baseline Report for FY 2022–23.
- Purpose: To assess panchayat performance across themes such as governance, transparency, service delivery, and financial management.
- The index tracks the progress of Panchayats based on nine Localized SDGs (LSDGs). These themes aim to bring global goals into rural realities, fostering localized and inclusive development strategies.

The Global Impact of Measles Vaccination on
- Pre-vaccine era: Measles was extremely common — over 90% of children got infected. Around 25% of symptomatic cases were hospitalized. In the U.S. alone, ~50,000 hospitalizations and hundreds of deaths occur annually.
- Vaccine breakthrough: In 1963, John Enders developed the first effective vaccine. High-income countries rapidly adopted it; global scale-up followed in the 1970s and 1980s.
- Lives saved: In the last 50 years, over 9 crore (90 million) deaths have been prevented globally due to the measles vaccination.
- Effectiveness: Studies show that vaccines reduce the risk of developing measles by 20 times.
- Other contributing factors: Prior to vaccine introduction, declining deaths in the U.S. were due to better treatment, nutrition, and sanitation, but these did not reduce infection rates, since measles is airborne and extremely contagious. · Global inequality: Measles deaths persisted in Africa and Southeast Asia throughout the 2000s due to low vaccination coverage. Case fatality rates in low-income countries were as high as 5–10% in the 1980s.
- Vaccination drive: Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) in the 1970s. By the early 2000s, over 9 crore children (~60%) were vaccinated. The Gavi Vaccine Alliance (2000) helped improve access in poorer countries.
- Current scenario: Over 100 million infants are vaccinated annually (~80% coverage). 2.9 crore lives saved in Africa and 2.0 crore in Southeast Asia, making measles vaccination one of the most successful public health efforts in history.
NEP 2020 and the TransformaƟ on of Indian EducaƟ on System
NEP 2020 is a landmark structural reform aimed at transforming Indian education. system through innovation, employability, and global competitiveness.
It promotes:
- Flexible four-year undergraduate programmes
- MulƟ ple entry-exit options
- Vocational training and industry internships
- Academic credits and skill certifications
Employability Focus:
- Internships and vocationalization improve real-world skills.
- Apprenticeships supported by the government stipends bridge the industry-academia gap.
- Over 3.6 lakh students have already been placed in internships. o
- Increasing number of insƟ tuƟ institutions adopting interdisciplinary practical curricula.
Research & Innovation Boost:
- R&D cells are set up in over 350 institutions.
- Patents filed by HEIs rose by 158% (2021–23).
- Initiatives like the ANRF Act 2023, AICTE IDEA Labs, and SPARC facilitate collaborative global research.
- Promotion on of Indian Knowledge Systems (IKS) to nurture indigenous thinking.
- Smart India Hackathon engaged over 13.9 lakh students.
Global Competitiveness:
- 11 Indian universities in Quacquarelli Symonds QS Global Top 500.
- 163 Indian universities in QS Asia Rankings 2025.
- 10 He is in the global top 50 by discipline.
- Improved ranking in the Global Innovation Index from 76 (2013) to 39 (2023).
Employment Trends:
- Youth employment (15–29 years) rose post-2018–19.
- Female employment increased to 30.7% in 2023–24.
- Decline in casual labour; rise in regular/formal jobs for both genders.
- Shift indicates a move towards more structured, sustainable, and better-paying jobs.
NEP 2020 is driving a paradigm shiŌ in India’s educaƟ on system — blending academic excellence with employability, research, innovation, and global relevance. It is crucial to India’s aspiraƟ ons of becoming a knowledge economy and achieving demographic dividend.

