Seaweed Farming in India
What is seaweed?
- The Seaweeds are macrophytic algae, a primitive type of plants lacking true roots, stems and leaves. Seaweeds are wonder plants of the sea and highly useful plants.
- Seaweeds grow in the shallow waters. Root system and conducting tissues like land plants are absent in seaweeds.
 Major seaweed classification
Major seaweed classification- Four groups of seaweeds are recognized according to their pigments that absorb light of particular wave lengths and give them their colours of green, blue, brown and red.
1.The Chlorophyta (green algae)
2.The Phaeophyta (brown algae)
3.The Rhodophyta (red algae)
- There are about 900 species of green seaweed, 4000 red species and 1500 brown species found in nature.
Seaweed Farming
- The practice of cultivating and harvesting seaweed
1.Simplest form: The management of naturally found batches
2.Most advanced form: Fully controlling the life cycle of the algae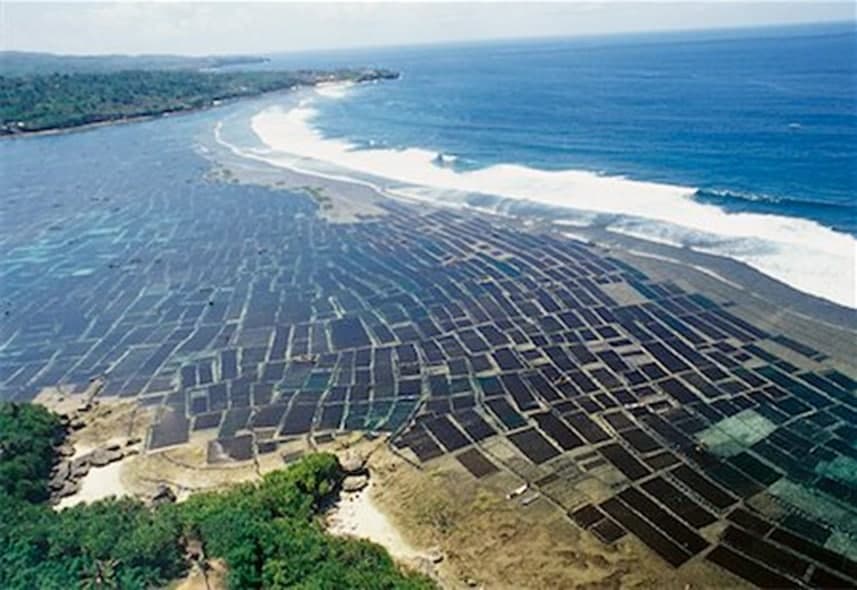

Important Species
The green seaweeds Enteromorpha, Ulva, Caulerpa and Codium are utilized exclusively as source of food (eaten as fresh salads or cooked as vegetables along with rice).
Anti-viral compounds from Undaria sp. have been found to inhibit the Herpes simplex virus, which are now sold in capsule form.
- Research is now being carried out into some of Seaweed Species extract to treat breast cancer, HIV and agglutinates human B-type erythrocytes in vitro.
Methods of cultivation
- Single Rope Floating Raft method (Coir Rope & Nylon Rope).
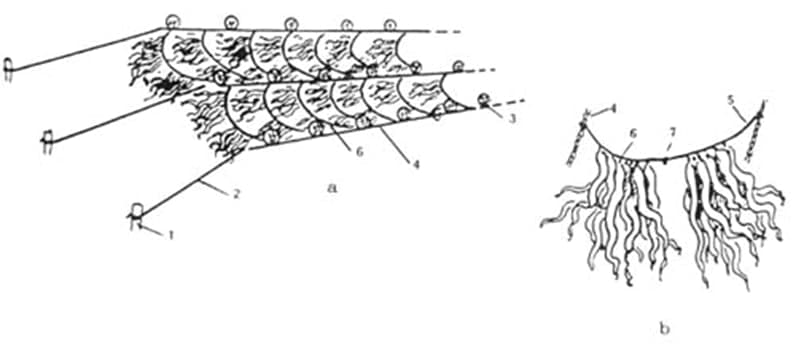
Fixed Bottom long line method (Coir Rope & Nylon Rope).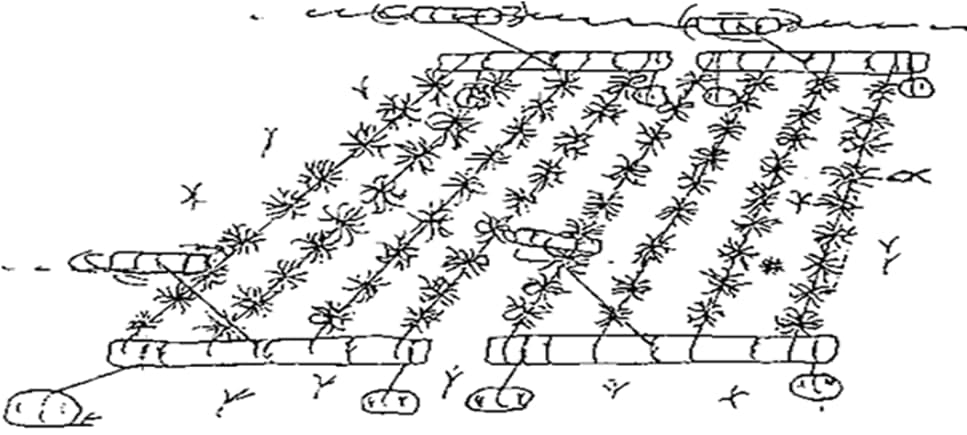 Integrated Multi Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) method.
Integrated Multi Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) method. What are the advantages
What are the advantages
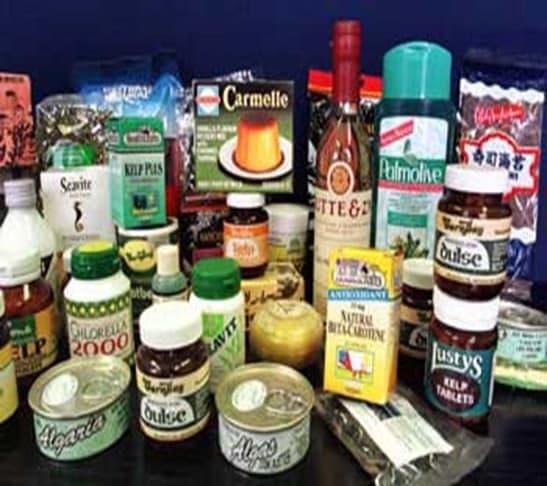
Seaweeds new renewable source of food, energy, chemicals and medicines. Provides valuable source of raw material for industries like health food, medicines, pharmaceuticals, textiles, fertilizers, animal feed etc.
Used for production of Agar, Alginates & Carrageenan. Chemicals from brown seaweeds such as alginic acid, mannitol, laminarin, fucoidin and iodine have been extracted successfully on a commercial basis.
- Seaweeds were rich in minerals, vitamins, trace elements and bioactive substances, seaweeds are called medical food of the 21st century.
What does it contribute
- Economic importance: Some 221 species of seaweed are utilized commercially. Of these, about 145 species are used for food and 110 species for phycocolloid production.
- Inadequate natural seaweed to meet the industrial requirements and hence cultivation of these important resources has become necessary.
- Asia stands as the world leader in seaweed cultivation and more than 80% is contributed by China, Korea and Japan.
- Recently, seaweed cultivation is picking up in certain coastal districts of the Tamil Nadu state.
What is the Indian scenario?
- Seaweeds grows abundantly along the Gujarat and Tamil Nadu coasts and around Andaman & Nicobar islands and Lakshadweep.
- There are also a presence of rich seaweed beds around Chilka in Odisha, pulicat in Tamil Nadu, Mumbai, Goa, Karwar, Varkala and Vizhinjam.
- Approximately 700 species of marine algae found in regions of the Indian coast, nearly 60 species are commercially important.
- seaweed is crucial in times when India pledged to improve emissions intensity of its GDP by 33-35% by 2030 below 2005 levels, under its INDC (Intended Nationally Determined Contributions).
- In 2012, the then Chief Minister of Gujarat, Narendra Modi, invited Gujarat Livelihood Promotion Company (GLPC) to join in to fight against high malnutrition levels in the state with the help of the seaweed farming
Budget 2021
- The Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has proposed in the Budget to set up a multi-purpose seaweed park in Tamil Nadu as part of promoting seaweed cultivation.
- Seaweed farming is an emerging sector with potential to transform the lives of coastal communities and will provide large employment and additional income.
For any Course Assistance please fill the form :