Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)
IRNSS
- Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
- IRNSS(NavIC) is an independent regional navigation satellite system designed by ISRO to provide position information in the Indian region and 1500 km around the Indian mainland.
IRNSS would provide two types of services:
- Standard Positioning Services available to all users.
- Restricted Services provided to authorised users.
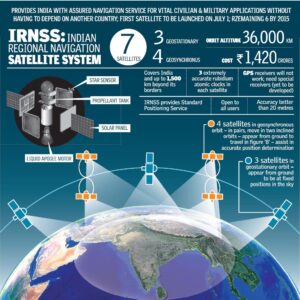
NavIC is a regional system and so its constellation will consist of 7 satellites
- 4 geosynchronous satellites in the Earth’s Atmosphere in pairs, move in two inclined orbits and appear from the ground to travel in Figure 8 – Assist in accurate position determination.
- 3 will be Geostationary Orbit – appearing from the ground to be fixed positions in the sky.
Applications:
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation.
- Disaster Management.
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management.
- Integration with mobile phones.
- Precise Timing.
- Mapping and Geodetic data capture.
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travellers.
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers.
Significance
- National security
- Reliability
- Accuracy
- Disaster management
- South Asian and Regional cooperation
Other Satellite Navigation Systems:
Global Positioning System (GPS):
- Initiated in 1978 and achieved global coverage in 1995 and is owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Air Force.
- It consists of 24 to 32 medium Earth orbit satellites in six different orbital planes.|
Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS)
- Operated by Roscosmos, a state corporation responsible for the space flight and cosmonautics program for the Russian Federation.
- It became operational in 1982 and achieved global coverage in 1996, and again in 2011 (after the system had fallen into disrepair).
- It has full global coverage with 24 satellites.
GALILEO
- It was initiated in 2005 by the European Space Agency and projected to provide global coverage by 2020 with 30 satellites.
Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
- It is operated by the Japanese government.
- It is a four-satellite regional time transfer system and enhancement for GPS covering Japan and the Asia-Oceania regions.
- Its services have been available on a trial basis since January 2018.