- IOD is the difference between the temperature of the eastern (Bay of Bengal) and the western Indian Ocean (Arabian Sea).
- This temperature difference results in pressure difference which results inflowing of winds between eastern and western parts of the Indian Ocean.
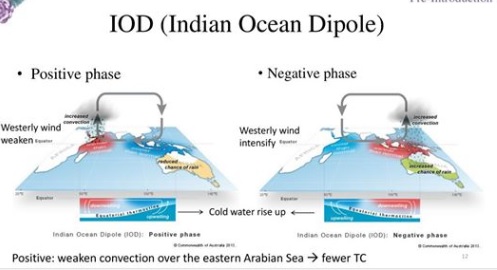
- A ‘positive IOD’ — or simply ‘IOD’ — is associated with cooler than normal sea-surface temperatures in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and warmer than normal sea-surface temperatures in the western tropical Indian Ocean.
- The opposite phenomenon is called a ‘negative IOD’ and is characterized by warmer than normal Sea Surface Temperature (SSTs) in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and cooler than normal SSTs in the western tropical Indian Ocean.
- Impacts:
- Studies have shown that a positive IOD year sees more than normal rainfall over central India.
- A negative IOD complements El Nino leading to severe drought.
- At the same time, Positive IOD results in more cyclones than usual in the Arabian Sea.
- Negative IOD results in stronger than usual cyclogenesis (Formation of Tropical Cyclones) in the Bay of Bengal. Cyclogenesis in the Arabian Sea is suppressed during this time.